Configuration Guide
Backend
Command-line Arguments
The Clutch binary will consume clutch-config.yaml in the current working directory by default.
To use a different path for the configuration,use the -c option, e.g.
./clutch -c /etc/clutch/clutch-config.yaml
Config Features
Clutch supports the expansion of environment variables after reading the YAML when the gateway starts up.
password: ${MY_SECRET_PASSWORD}
YAML Specification
All backend configuration in Clutch is specified in protobuf definitions. For information on how YAML and JSON map to protobuf see Language Guide (proto3): JSON Mapping.
Note: it is recommended to write YAML long-form, the format of the examples below are shortened for documentation purposes.
Gateway
See api/config/gateway/v1/gateway.proto for the full configuration specification. For an example of a filled-in config, see the sample clutch-config.yaml.
Top-level Configuration
gateway: {<GatewayOptions>}
services: [{<Service>}, ...]
resolvers: [{<Resolver>}, ...]
modules: [{<Module>}, ...]
extends: ["<string>", ...]
GatewayOptions
listener: {<Listener>}
json_grpc_loopback_listener: {<Listener>}
logger: {<Logger>}
stats: {<Stats>}
timeouts: {<Timeouts>}
middleware: [{<Middleware>}, ...]
assets: {<Assets>}
enable_pprof: <bool>
accesslog: {<clutch.config.middleware.accesslog.v1.Config>}
max_response_size_bytes: <uint32>
secure_cookies: {<google.protobuf.BoolValue>}
Module, Resolver, Service
Modules, resolvers, and service are all specified using the same format. The name of the component is specified, and if necessary the config is provided via the Any type in thetyped_config field.
See comments in any.proto from the protobuf project for additional documentation.
name: "<string>"
typed_config: {<google.protobuf.Any>}
Example with clutch.service.authn and environment variables.
...
services:
- name: clutch.service.authn
typed_config:
"@type": types.google.com/clutch.config.service.authn.v1.Config
oidc:
issuer: ${OIDC_ISSUER}
client_id: ${OIDC_CLIENT_ID}
client_secret: ${OIDC_CLIENT_SECRET}
redirect_url: "http://localhost:8080/v1/authn/callback"
session_secret: ${AUTHN_SESSION_SECRET}
...
For now, docs for each component's configuration are not auto-generated. In order to determine the configuration specification for a component, check at the well-known path in api/config/
In the example above, the configuration schema is specified in api/config/service/authn/v1/authn.proto.
Frontend
The Clutch frontend requires configuration at build time to determine which installed workflows to register and allows for users to override default values.
A custom gateway generated from the scaffolding tool will have a register-workflows script target in frontend/package.json. This script calls out to @clutch-sh/tools to parse the custom gateway's config file and register the found workflows. It expects the frontend config file at the path frontend/src/clutch.config.js.
Example:
module.exports = {
"@clutch-sh/ec2": {
terminateInstance: {
trending: true,
componentProps: {
resolverType: "clutch.aws.ec2.v1.Instance",
},
},
resizeAutoscalingGroup: {
componentProps: {
resolverType: "clutch.aws.ec2.v1.AutoscalingGroup",
},
},
},
"@lyft/private-workflow": {
example: {},
},
};
In the configuration above there are some open source workflows registered, in this case with overrides for their trending values. Notice how these workflows also have a componentProps field specified. Some workflows will require prop values that are specific to the user. Without them the workflow will not register on the app even if listed in the config file. Take the @clutch-sh/ec2 package as an example; both the terminateInstance and resizeAutoscalingGroup workflows require a resolverType prop.
If a config is invalid a warning will be emitted in the console denoting which workflow is misconfigured along with the which required props are missing, for example:
[@clutch-sh/ec2][instance/terminate] Not registered:
Invalid config - missing required component props resolverType
It's important to note that only packages which are installed will be included, even if they are listed in the config file.
Note that Clutch uses the following architecture with component props:
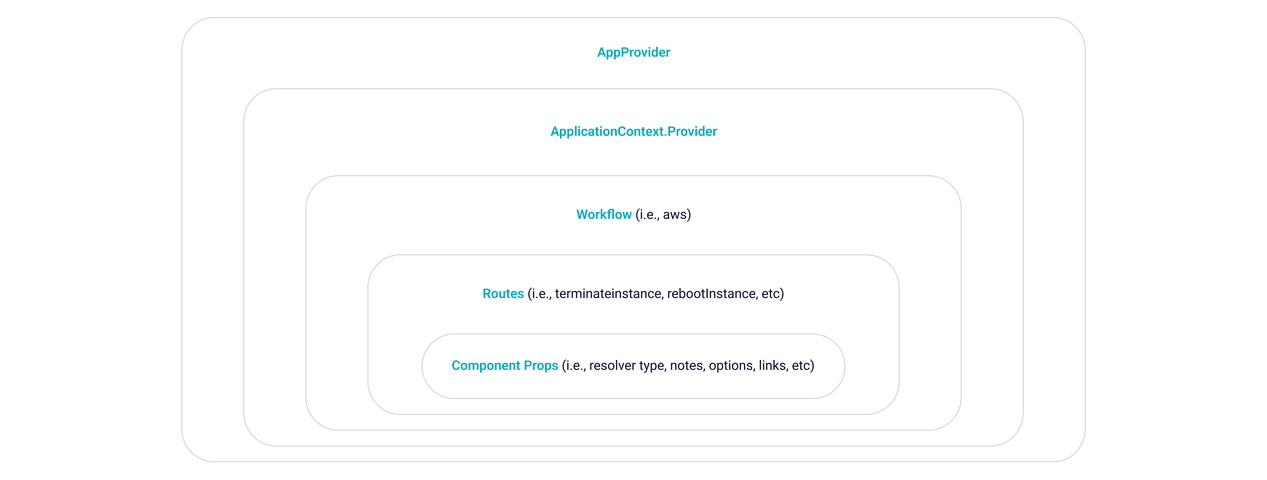 It is convenient for specific routes to be able to specify their own props without having to worry about storing workflow props in a central location. Component props can be used for transforming string inputs, specifying options, or anything that is route specific.
It is convenient for specific routes to be able to specify their own props without having to worry about storing workflow props in a central location. Component props can be used for transforming string inputs, specifying options, or anything that is route specific. For more context, see the code here.